🎯 TL;DR: A closed-loop and sample-efficient RFT framework for diffusion-based planners.
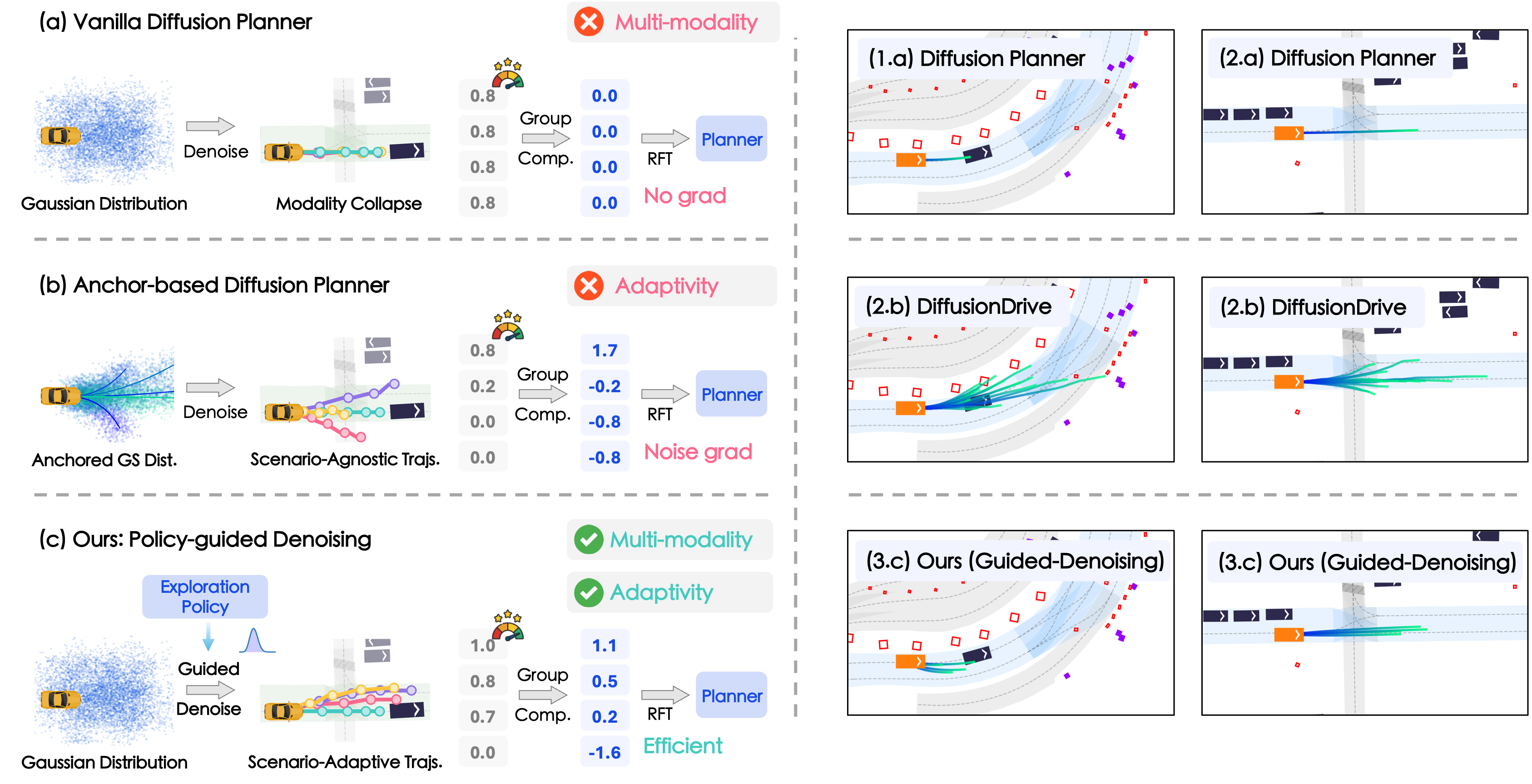
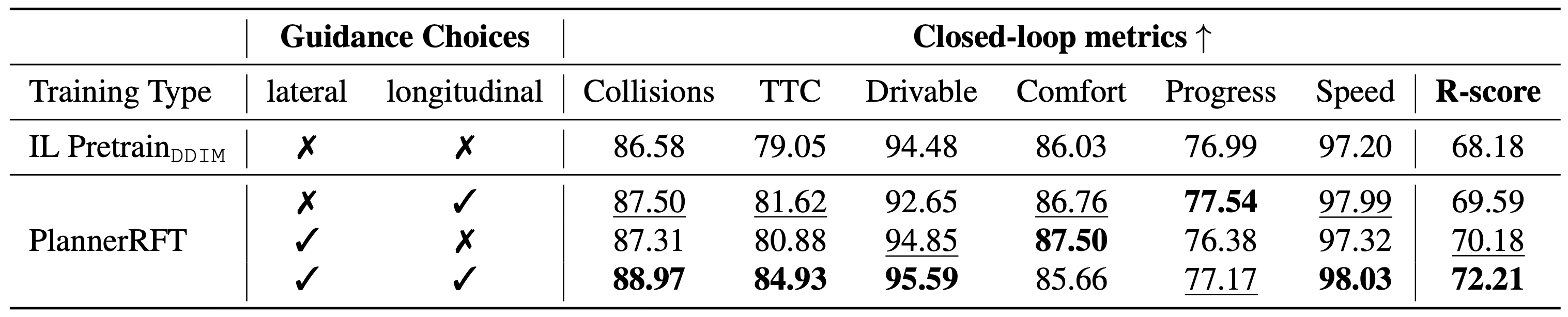
📐 Orthogonal Guided Denoising. An orthogonally decoupled guided denoising strategy that perturbs lateral displacement and longitudinal velocity around a reference trajectory, facilitating diverse and continuous trajectory sampling.
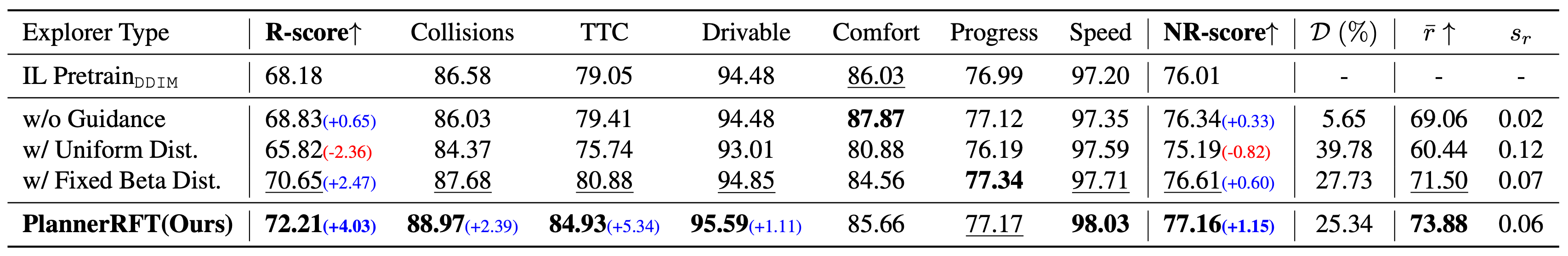
🧭 Scenario-Adaptive Exploration. A learnable exploration policy that dynamically adjusts the denoising process based on the current scenario, toward more promising exploration thus improving sample-efficiency.
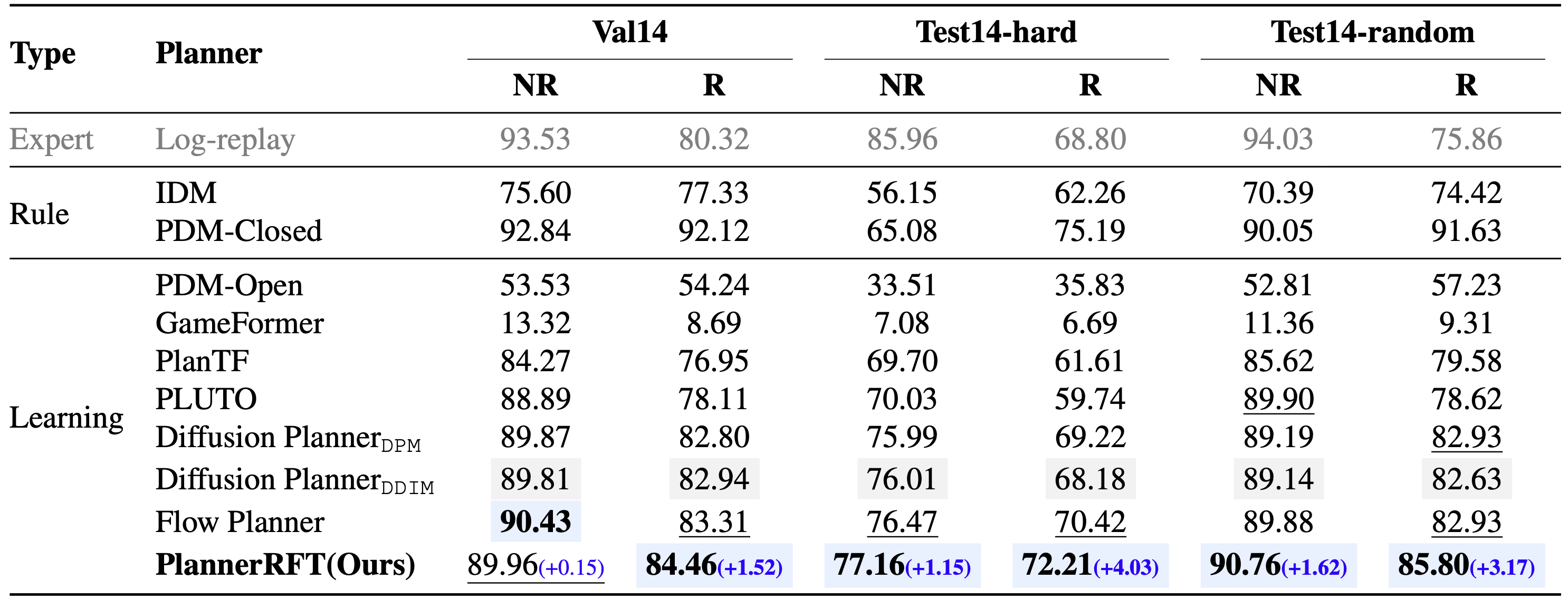
🔁 Closed-Loop Optimization. A dual-branch optimization framework that jointly refines trajectory distributions and the exploration policy through closed-loop rollouts.