
Pseudo-Expert Scene Simulation. (a) Trajectory perturbation on T to T + H, (b) reactive environment rollout, and pseudo-expert trajectory generation from T + H to T + 2H under recovery-based and planner-based strategies.
*: pseudo-expert supervision; †: reward scoring; S.: per-stage EPDM score.
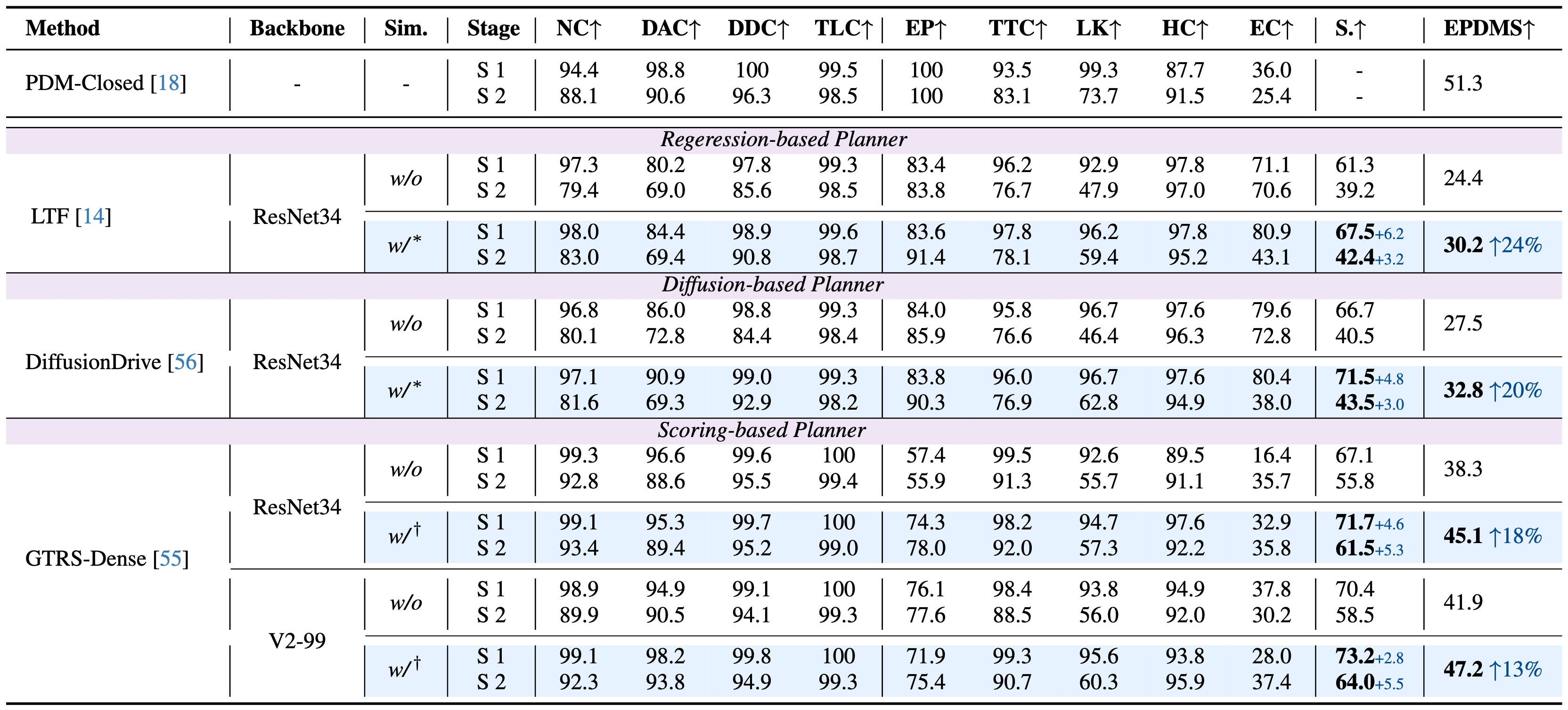
*: pseudo-expert supervision; †: reward scoring.
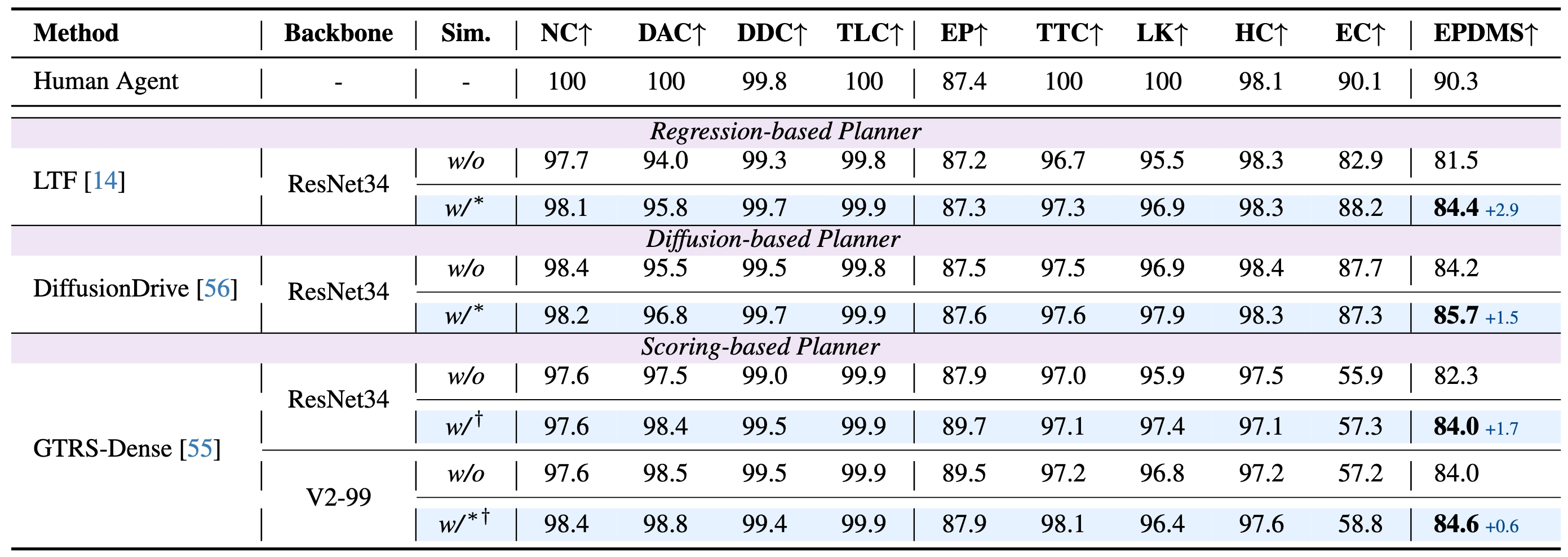
S1/2: Per-stage score; recovery/planner: recovery-based/planner-based expert; reward: reward scoring only; *: ensemble
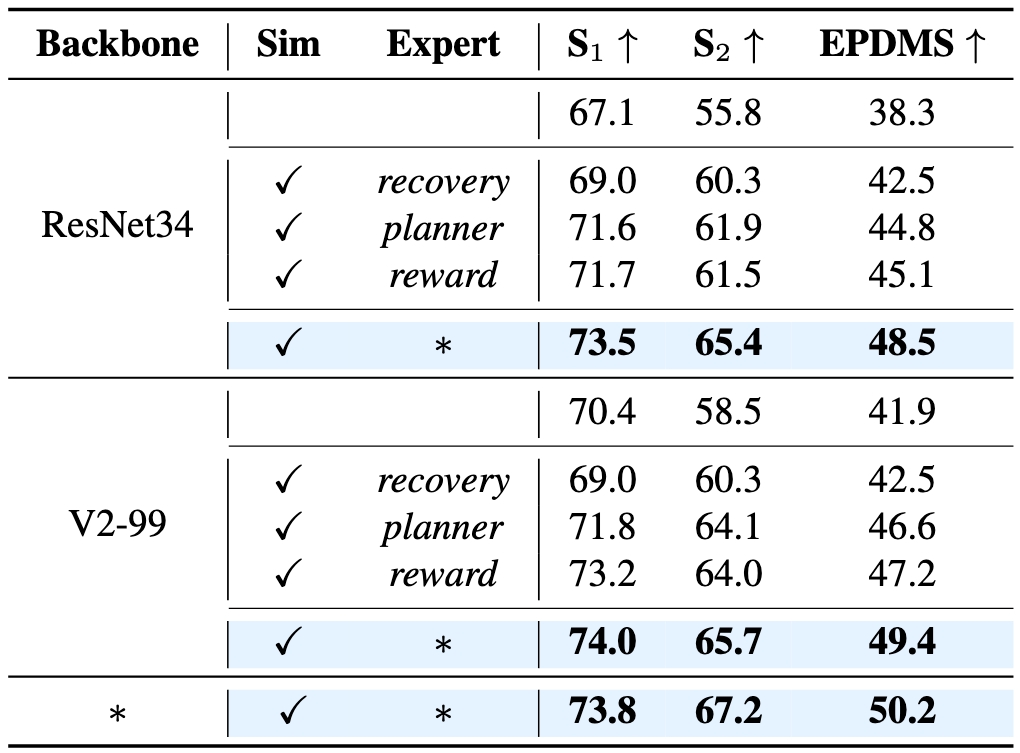
S1/2: per-stage score.
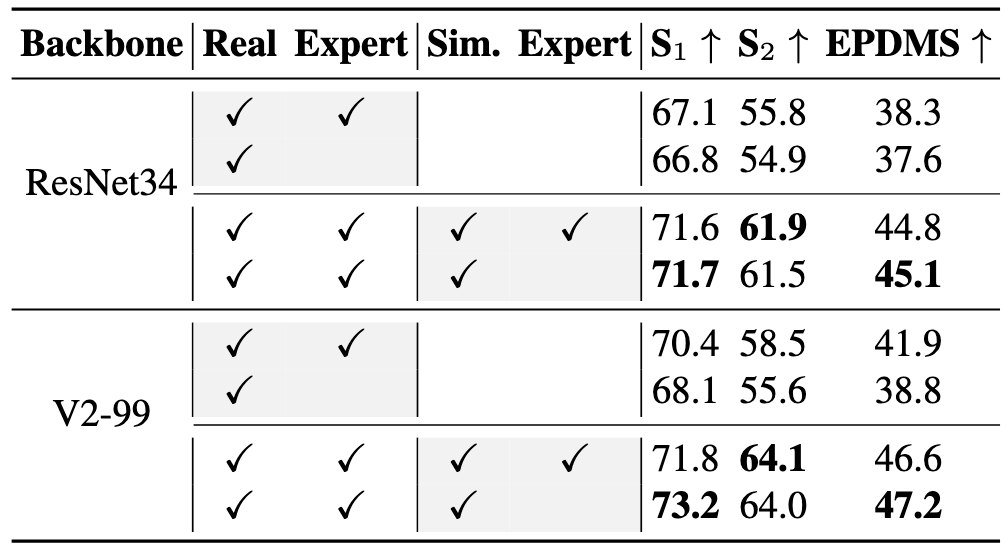
#Round: sampling rounds; #Sim.: simulation data number.
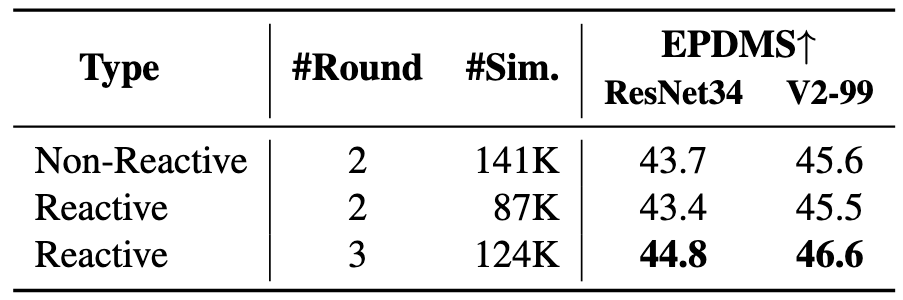
#R: sampling rounds; EPDMS on navhard.
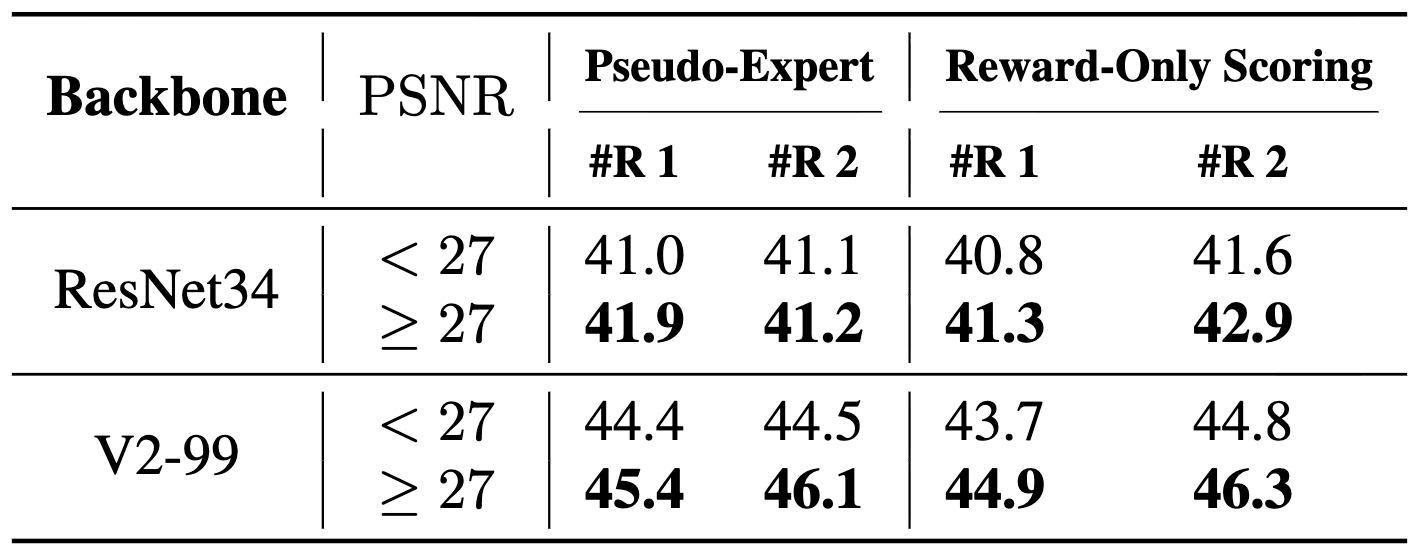
Scaling Dynamics with Varying Simulation Data aross End-to-End Planners and Pseudo-Experts.
💡 Pseudo-Expert Should Be Exploratory.
💡 Multi-Modality Modeling Sparks Scaling.
💡 Reward is All You Need.
Scaling Dynamics with Varying Real-World Data across End-to-End Planners.
💡 Sustained Simulation Gains Across Real Data Scales.
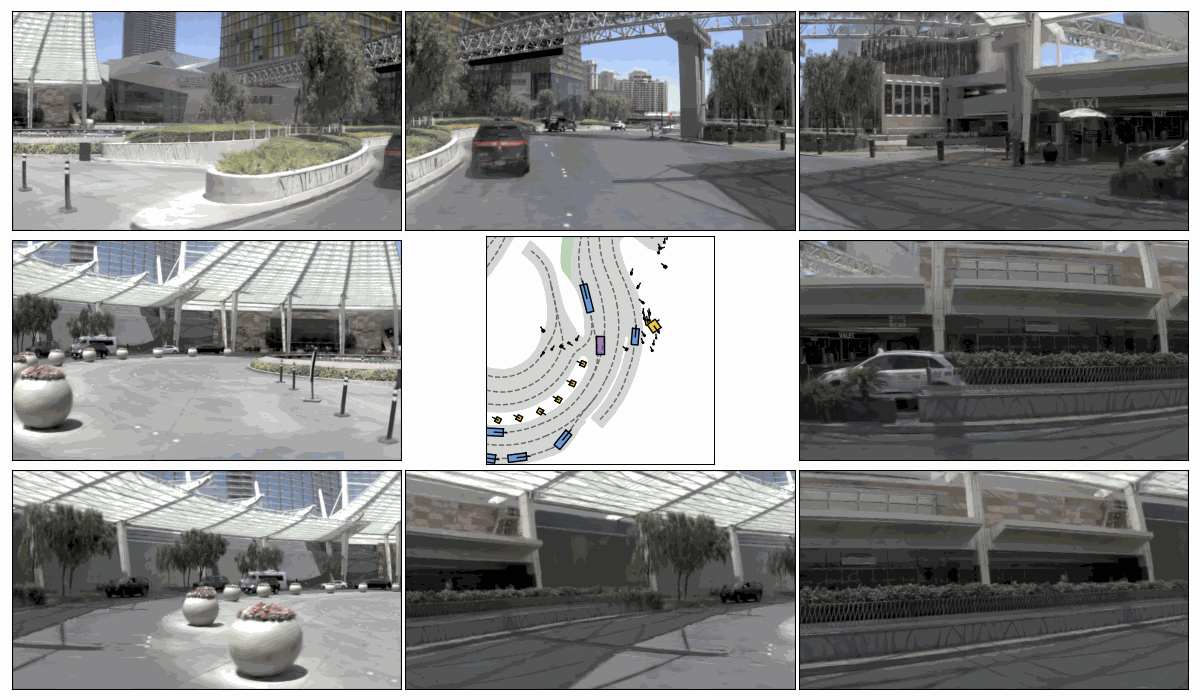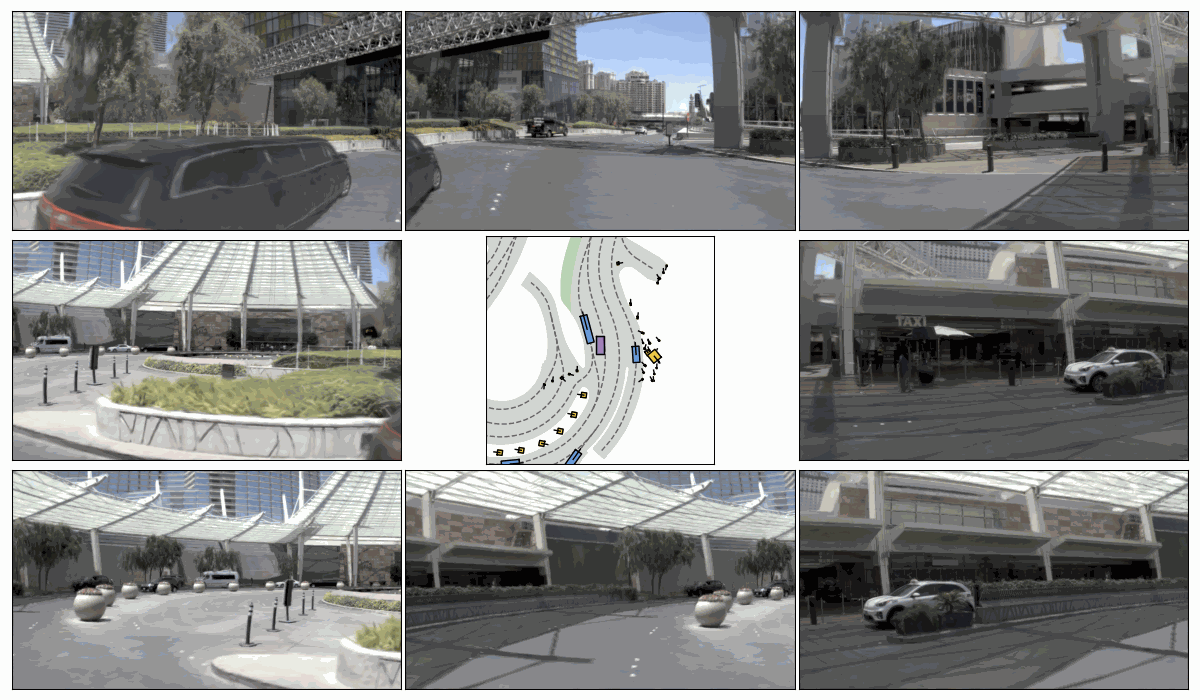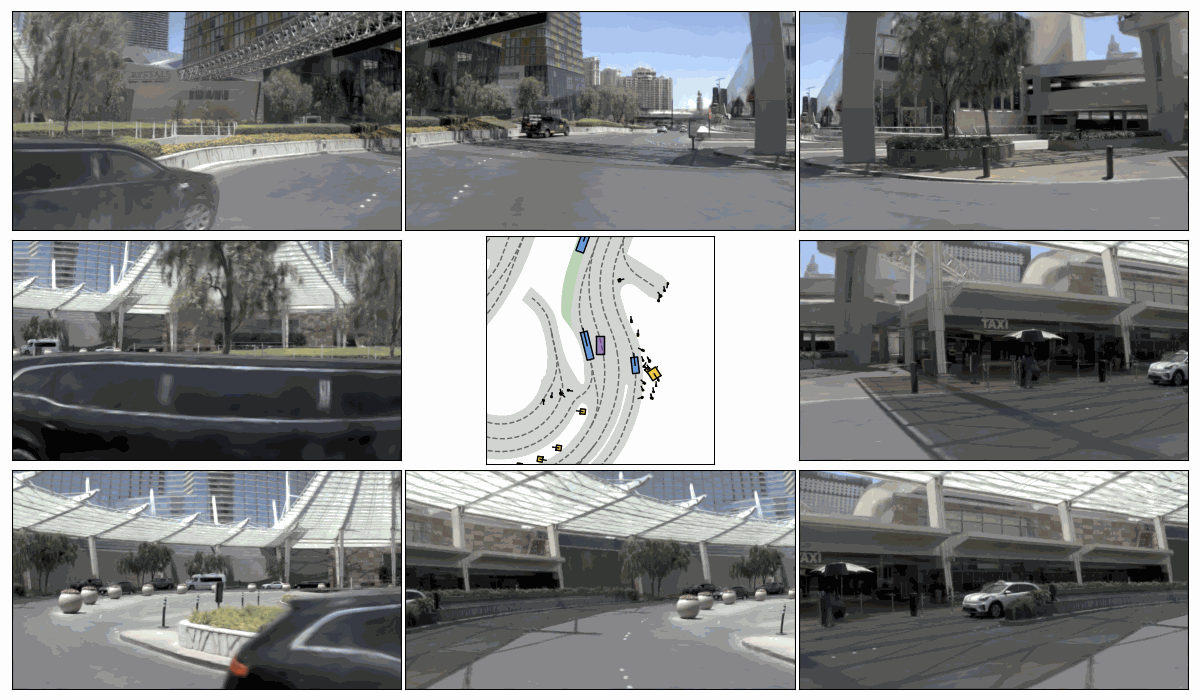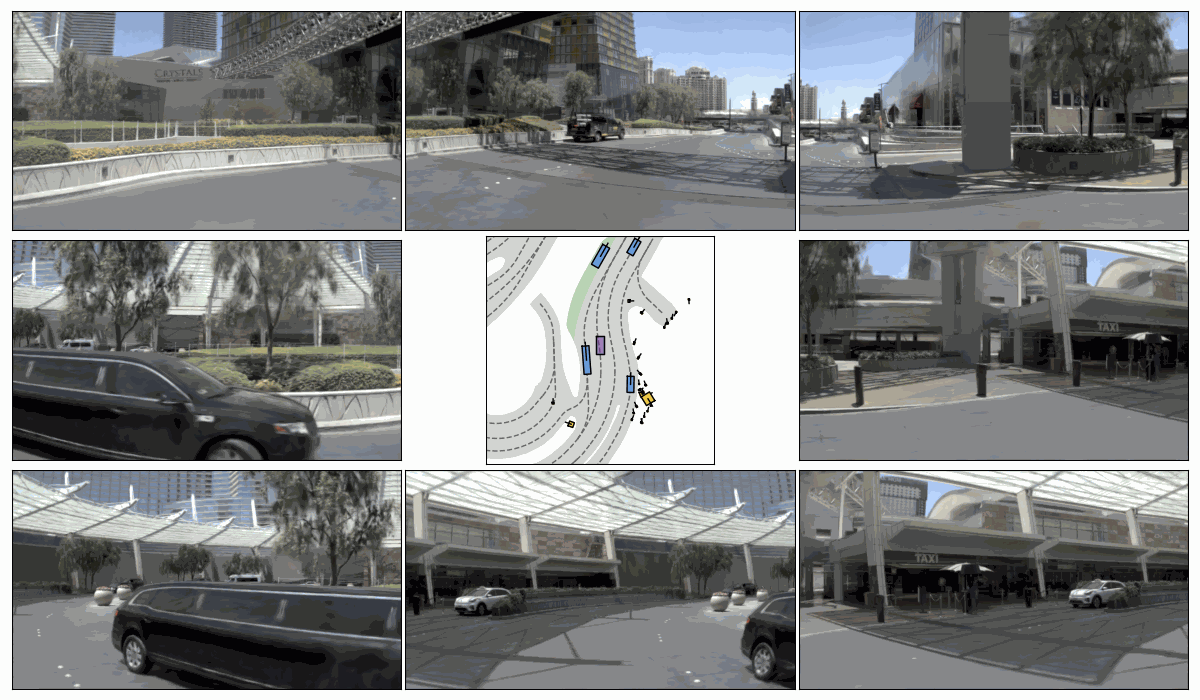
Sim. 1
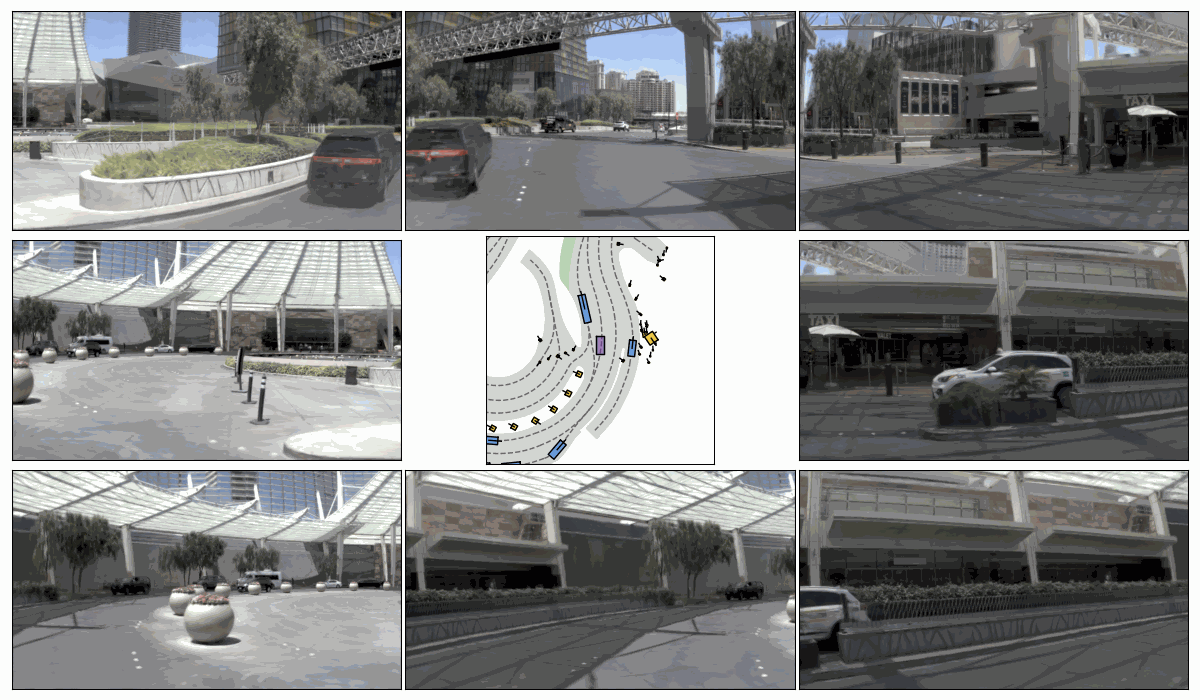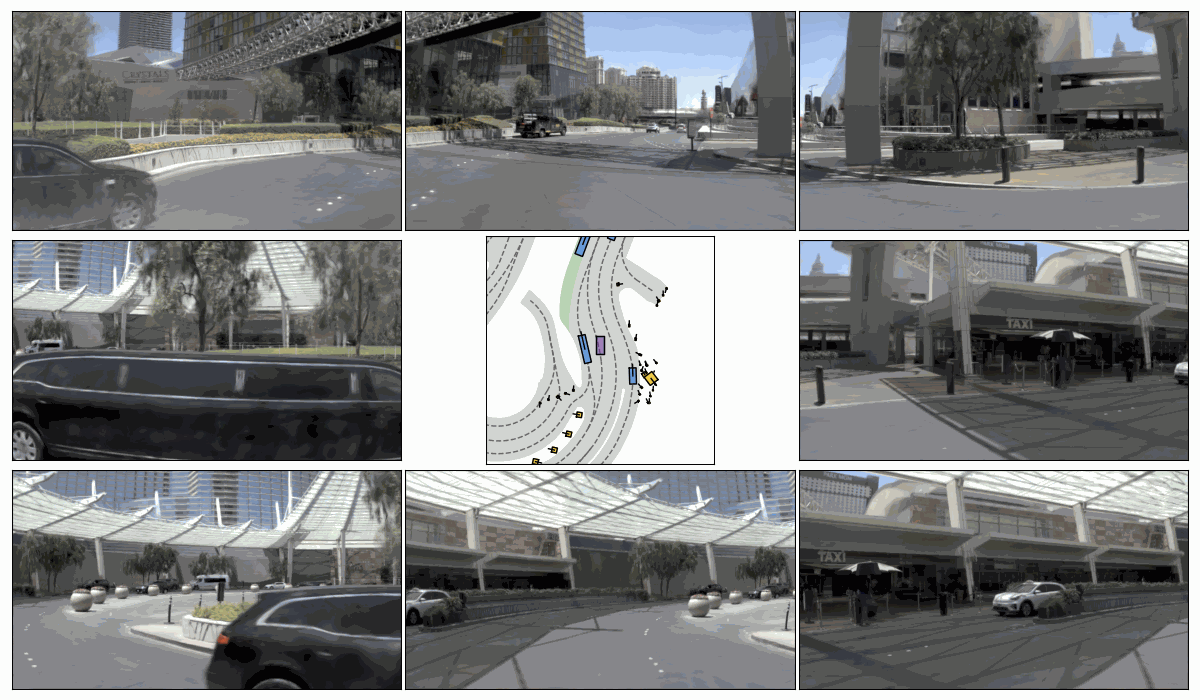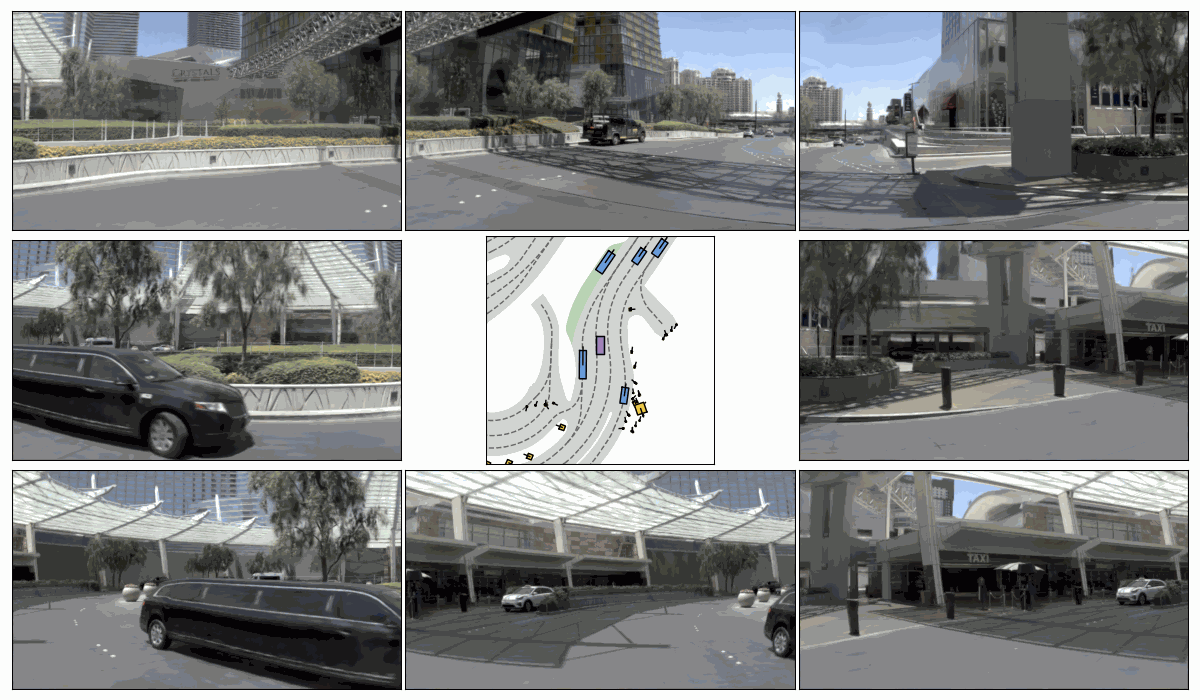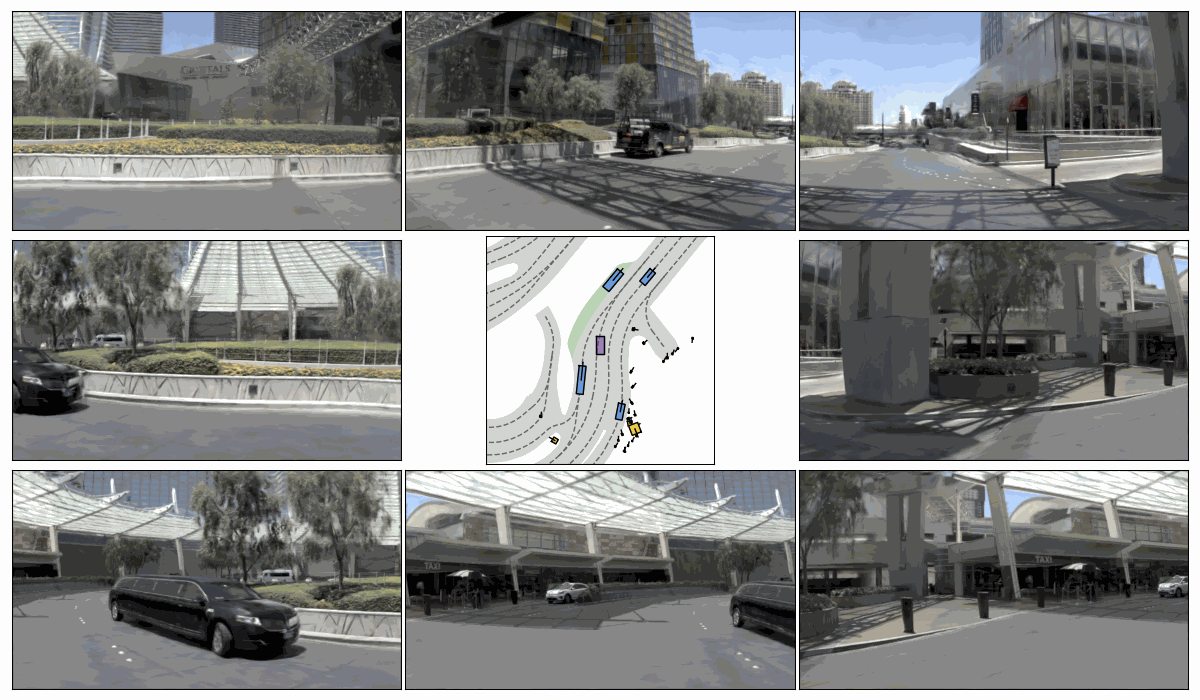
Sim. 2
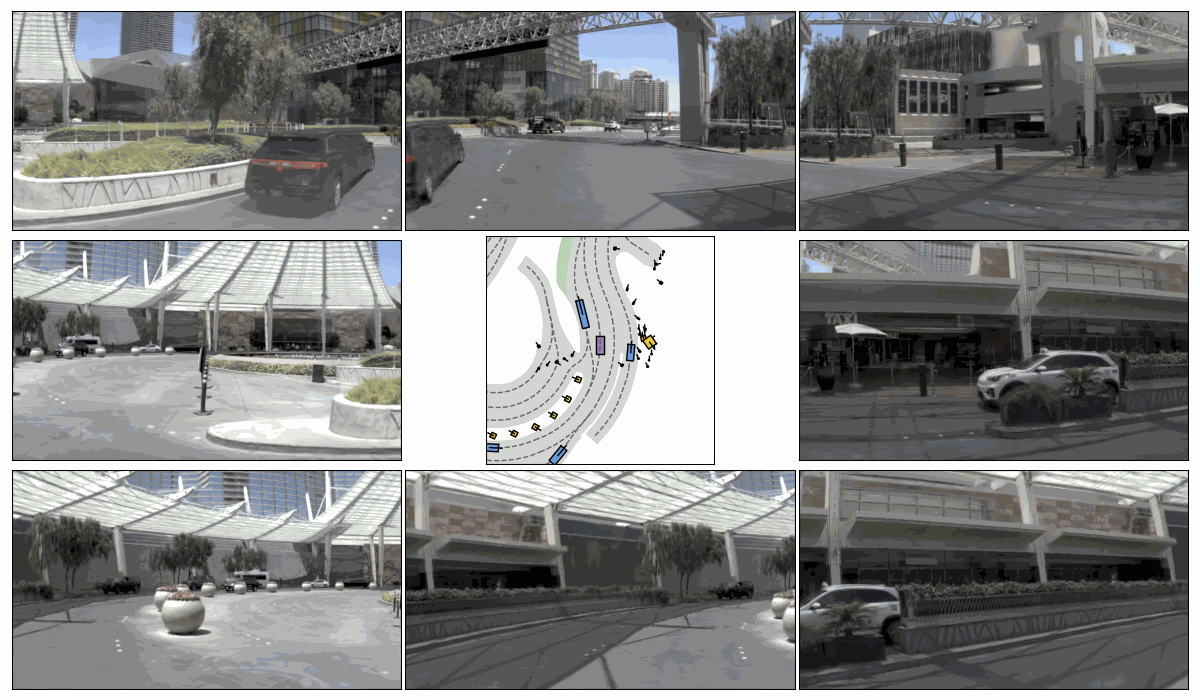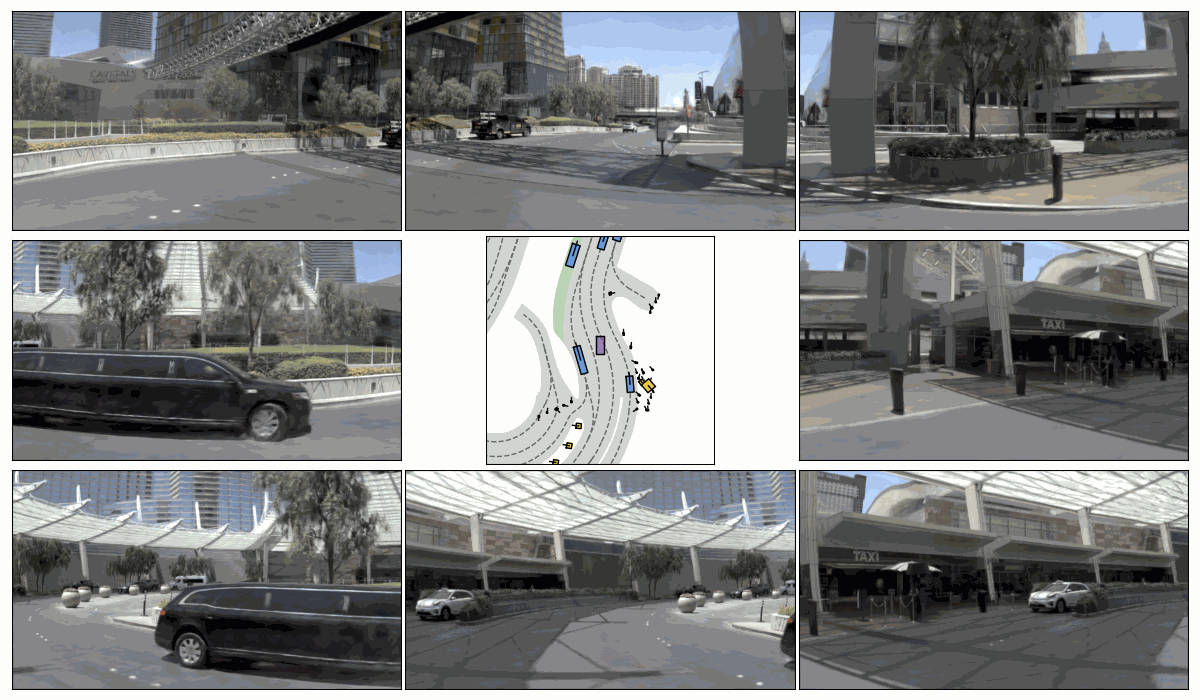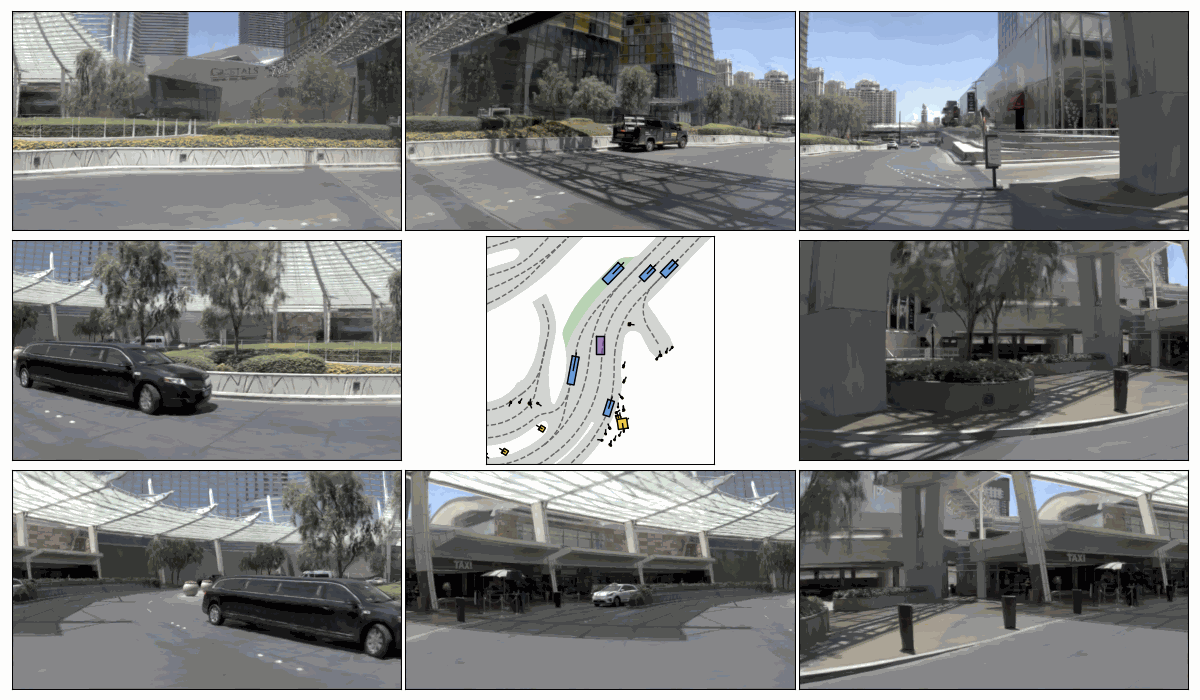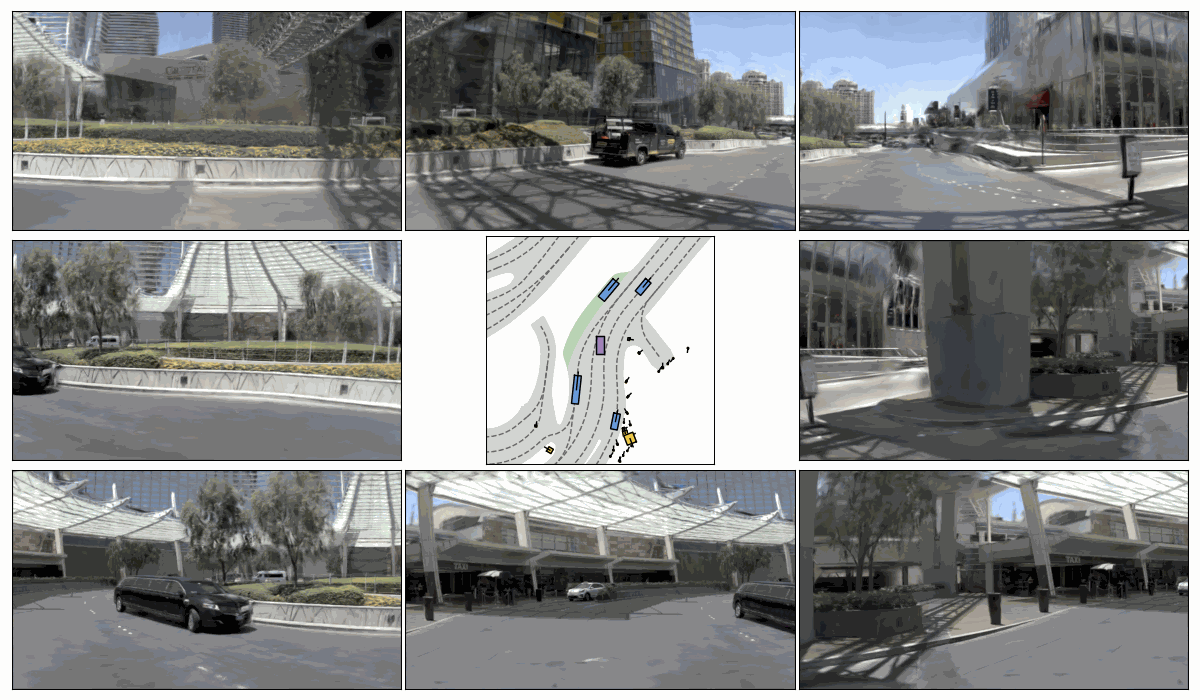
Sim. 3
@article{tian2025simscale,
title={SimScale: Learning to Drive via Real-World Simulation at Scale},
author={Haochen Tian and Tianyu Li and Haochen Liu and Jiazhi Yang and Yihang Qiu and Guang Li and Junli Wang and Yinfeng Gao and Zhang Zhang and Liang Wang and Hangjun Ye and Tieniu Tan and Long Chen and Hongyang Li},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2511.23369},
year={2025}
}